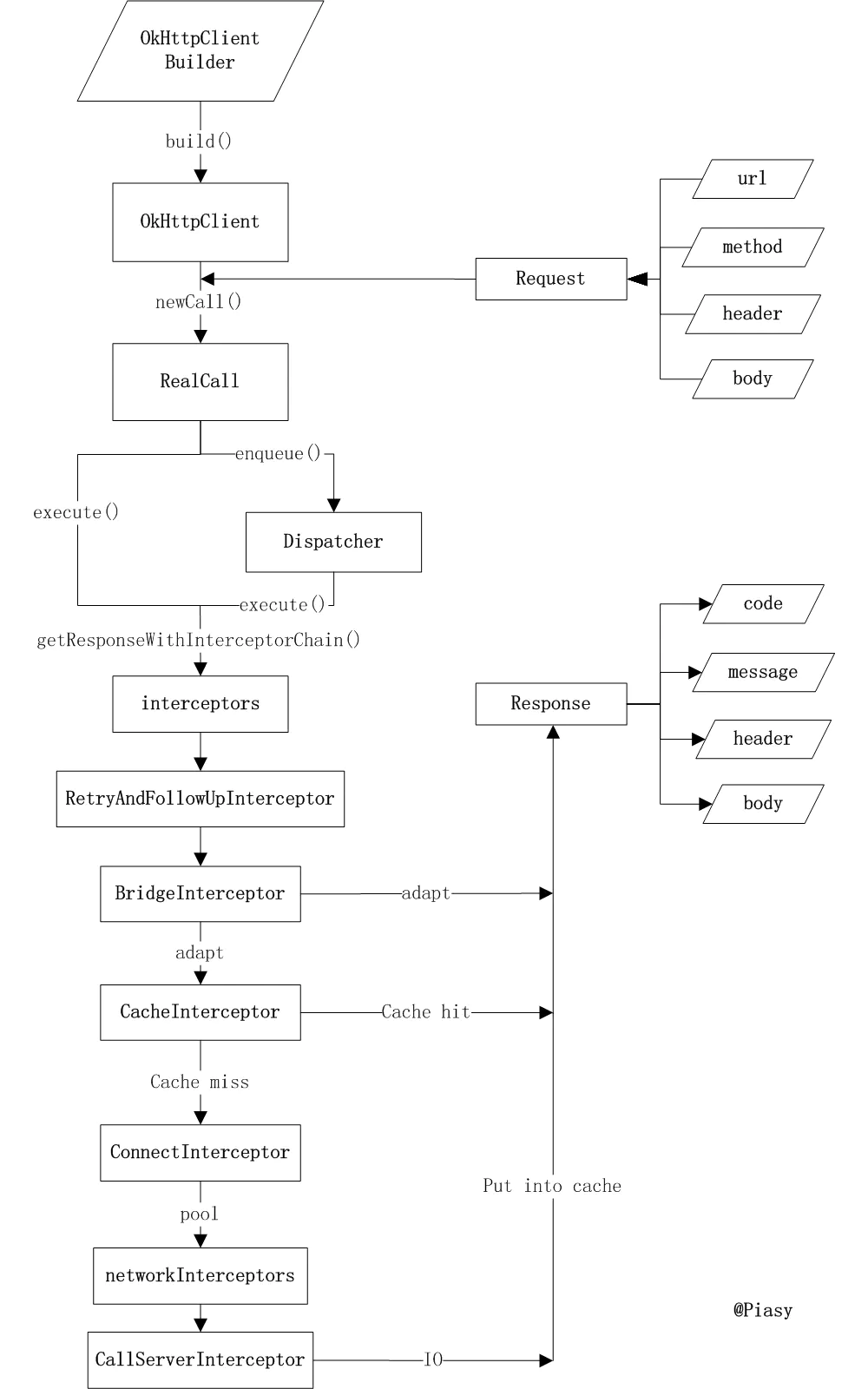
基本使用
同步和异步执行
@Override public Response execute() throws IOException {
synchronized (this) {
if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");
executed = true;
}
captureCallStackTrace();
eventListener.callStart(this);
try {
//加入同步队列
client.dispatcher().executed(this);
Response result = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
if (result == null) throw new IOException("Canceled");
return result;
} catch (IOException e) {
eventListener.callFailed(this, e);
throw e;
} finally {
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}
@Override public void enqueue(Callback responseCallback) {
synchronized (this) {
if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");
executed = true;
}
captureCallStackTrace();
eventListener.callStart(this);
//加入异步队列
client.dispatcher().enqueue(new AsyncCall(responseCallback));
}
Dispatcher内部有三个队列:
runningSyncCalls进行中的同步请求runningAsyncCalls进行中的异步请求。使用ExecutorService线程池,默认核心线程数为0,最大线程数Max,任务队列为空。readyAsyncCalls异步请求等待队列,超过最大请求数64,或者同一个服务端超过5个正在运行的请求,则加入等待队列。
连接复用
基于HTTP2的多路复用,一个连接可以承载多个流,一个连接可以发出多次请求,并且服务端可以响应多次
- 每个Call对应一个StreamAllocation
- Allocation从ConnectionPool查找可用连接RealConnection,当Address相同,且该连接的allocations数量小于限制,表示可用连接,保存到StreamAllocation中(StreamAllocation通过该连接进行通信),同时将StreamAllocation加入到RealConnection中的弱引用列表allocations中(表示该连接上有多少个流)
- 如果没有则新建,并入池
ConnectionPool中维护了一个RealConnection队列,RealConnection中封装了Socket、Buffer、路由、握手信息等
public final class RealConnection extends Http2Connection.Listener implements Connection {
//连接池
private final ConnectionPool connectionPool;
//一个连接可以承载多少个流,根据Http2协议设置
public int allocationLimit = 1;
//该连接承载的流
public final List<Reference<StreamAllocation>> allocations = new ArrayList<>();
}
ConnectionPool遍历RealConnection列表,判断连接是否可重用
public final class ConnectionPool {
@Nullable RealConnection get(Address address, StreamAllocation streamAllocation, Route route) {
assert (Thread.holdsLock(this));
//遍历池中的连接
for (RealConnection connection : connections) {
//判断连接是否可重用
if (connection.isEligible(address, route)) {
streamAllocation.acquire(connection, true);
return connection;
}
}
return null;
}
}
连接是否可重用:
- 连接上的流未超过承载限制
- 比较host或者路由信息
public final class RealConnection extends Http2Connection.Listener implements Connection {
...
public boolean isEligible(Address address, @Nullable Route route) {
// If this connection is not accepting new streams, we're done.
if (allocations.size() >= allocationLimit || noNewStreams) return false;
// If the non-host fields of the address don't overlap, we're done.
if (!Internal.instance.equalsNonHost(this.route.address(), address)) return false;
// If the host exactly matches, we're done: this connection can carry the address.
if (address.url().host().equals(this.route().address().url().host())) {
return true; // This connection is a perfect match.
}
// 1. This connection must be HTTP/2.
if (http2Connection == null) return false;
// 2. The routes must share an IP address. This requires us to have a DNS address for both
// hosts, which only happens after route planning. We can't coalesce connections that use a
// proxy, since proxies don't tell us the origin server's IP address.
if (route == null) return false;
if (route.proxy().type() != Proxy.Type.DIRECT) return false;
if (this.route.proxy().type() != Proxy.Type.DIRECT) return false;
if (!this.route.socketAddress().equals(route.socketAddress())) return false;
// 3. This connection's server certificate's must cover the new host.
if (route.address().hostnameVerifier() != OkHostnameVerifier.INSTANCE) return false;
if (!supportsUrl(address.url())) return false;
// 4. Certificate pinning must match the host.
try {
address.certificatePinner().check(address.url().host(), handshake().peerCertificates());
} catch (SSLPeerUnverifiedException e) {
return false;
}
return true; // The caller's address can be carried by this connection.
}
}
默认最大空闲连接为5,最长空闲连接为5分钟。
public final class ConnectionPool {
// 使用缓存线程池,实际上每次只会有一个清理任务,之所以不使用单线程池,是因为单线程池核心数为1,无法被回收
private static final Executor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
0 /* corePoolSize */,
Integer.MAX_VALUE /* maximumPoolSize */,
60L /* keepAliveTime */,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
Util.threadFactory("OkHttp ConnectionPool", true));
// 默认最大空闲连接为5,最大空闲时长为5分钟,可自定义
public ConnectionPool() {
this(5, 5, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
}
public ConnectionPool(int maxIdleConnections, long keepAliveDuration, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
this.maxIdleConnections = maxIdleConnections;
this.keepAliveDurationNs = timeUnit.toNanos(keepAliveDuration);
if (keepAliveDuration <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("keepAliveDuration <= 0: " + keepAliveDuration);
}
}
}
清理算法:put的时候往线程池添加清理任务
- 超过5个空闲连接,或者超过5分钟,则清理,返回0继续清理下一个。
- 找到空闲最久的连接,如果空闲时间不足5分钟,则计算剩余时间,返回等待时间,wait阻塞唤醒
- 没有空闲连接,但是有正在使用的连接,则返回等待时间,wait等待5分钟后唤醒
- 如果没有空闲和正在使用的连接,则返回-1,退出清理。
- 下次put的时候再添加清理任务
public final class ConnectionPool {
void put(RealConnection connection) {
assert (Thread.holdsLock(this));
// 只会有一个清理任务
if (!cleanupRunning) {
cleanupRunning = true;
// 添加清理任务
executor.execute(cleanupRunnable);
}
connections.add(connection);
}
private final Runnable cleanupRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
// 死循环,直到连接数为0
while (true) {
// 如果空闲最久的时间不足5分钟,则计算剩余时间,返回等待时间,wait阻塞唤醒
long waitNanos = cleanup(System.nanoTime());
// 如果没有空闲和正在使用的连接,则返回-1,结束任务
if (waitNanos == -1) return;
if (waitNanos > 0) {
long waitMillis = waitNanos / 1000000L;
waitNanos -= (waitMillis * 1000000L);
synchronized (ConnectionPool.this) {
try {
ConnectionPool.this.wait(waitMillis, (int) waitNanos);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
}
}
}
}
};
long cleanup(long now) {
int inUseConnectionCount = 0;
int idleConnectionCount = 0;
RealConnection longestIdleConnection = null;
// 空闲最久的时间
long longestIdleDurationNs = Long.MIN_VALUE;
// 找到需要清理的连接,或者计算下一次清理的时间
synchronized (this) {
for (Iterator<RealConnection> i = connections.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
RealConnection connection = i.next();
// 连接正在使用,跳过
if (pruneAndGetAllocationCount(connection, now) > 0) {
inUseConnectionCount++;
continue;
}
// 空闲连接数量
idleConnectionCount++;
long idleDurationNs = now - connection.idleAtNanos;
// 找到空闲最久的连接
if (idleDurationNs > longestIdleDurationNs) {
longestIdleDurationNs = idleDurationNs;
longestIdleConnection = connection;
}
}
// 空闲连接数或空闲时长大于设置值时,清除连接
if (longestIdleDurationNs >= this.keepAliveDurationNs
|| idleConnectionCount > this.maxIdleConnections) {
connections.remove(longestIdleConnection);
} else if (idleConnectionCount > 0) {
// 还没到最大空闲时长,计算剩余时间
return keepAliveDurationNs - longestIdleDurationNs;
} else if (inUseConnectionCount > 0) {
// 没有空闲连接,但有正在执行的连接,隔5分钟唤醒再检查
return keepAliveDurationNs;
} else {
// 没有空闲连接和正在使用的连接,退出清理
cleanupRunning = false;
return -1;
}
}
closeQuietly(longestIdleConnection.socket());
// 每次清理空闲最久的连接,返回0,继续检查第二名连接
return 0;
}
}
连接超时
默认超时时间:
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.connectTimeout(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.callTimeout(120, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.pingInterval(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.readTimeout(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.writeTimeout(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
责任链
Builder、责任链模式
interceptors # 自定义应用拦截器
-->RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor # 重试和跟进,创建StreamAllocation
-->BridgeIntercept # 添加各种头
-->CachedIntercept # 判断是否有缓存,或者取出缓存,使用LruDiskCache
-->ConnectionIntercept # 建立网络连接
-->NetworkIntercept # 自定义网络拦截器
-->CallServerInterceptor # 读写IO
应用拦截器
- 不需要关心像重定向和重试这样的中间响应。
- 总是调用一次,即使HTTP响应从缓存中获取服务。
- 监视应用原始意图。不关心OkHttp注入的像If-None-Match头。
- 允许短路并不调用
Chain.proceed()。 - 允许重试并执行多个
Chain.proceed()调用。
网络拦截器
- 可以操作像重定向和重试这样的中间响应。
- 对于短路网络的缓存响应不会调用。
- 监视即将要通过网络传输的数据。
- 访问运输请求的Connection。
Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException {
// Build a full stack of interceptors.
List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors());
interceptors.add(retryAndFollowUpInterceptor);
interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar()));
interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache()));
interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client));
if (!forWebSocket) {
interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors());
}
interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket));
Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, null, null, null, 0,
originalRequest, this, eventListener, client.connectTimeoutMillis(),
client.readTimeoutMillis(), client.writeTimeoutMillis());
return chain.proceed(originalRequest);
}
public class RealInterceptChain {
private final List<Interceptor> interceptors;
public Response proceed() {
RealInterceptorChain next = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, ..., index + 1);
//责任链,用于找到下一个处理者
Response response = interceptor.get(index).intercept(next);
}
}
public interface Interceptor {
Response intercept(Chain chain);
}
public class XXXInterceptor {
@Override
public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
//doSomething,发出请求之前,处理请求数据
//处理完之后交给责任链继续传递请求
Response networkResponse = chain.proceed(requestBuilder.build());
//doSomething,请求返回之后,处理返回数据
}
}
请求失败重试
OkHttpClient支持配置retryOnConnectionFailure,默认为true。通过RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor拦截器进行重试,根据上一个Response判断是否需要再次请求,例如重定向。
RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor只适用于部分场景
- 一个URL可能对应多个IP,一个IP的时候请求失败,重试其他IP
- 一个代理服务器请求失败的时候,重试其他代理服务器
- 过时的池连接
- 请求重定向
对于协议错误、握手失败、SSL验证失败等情况无法恢复请求,可以自定义拦截器重试
缓存
意义:
- 减少请求次数,减少服务器压力
- 本地数据读取更快,页面能够更快的显示
- 无网络情况下提供数据
缓存分类
按端分类:
- 客户端缓存
- 服务器缓存:CDN缓存、网关缓存
根据是否发出请求分类(重要!!!后面会频繁提到)
- 强制缓存:客户端验证缓存有效性,决定是否使用缓存
- 协商缓存(对比缓存):向服务器发送请求,由服务器验证缓存是否失效,决定是否可以使用缓存
Header缓存字段
expires:服务端返回的到期时间,客户端请求时判断是否到期,由于服务器和客户端时间可能存在误差,因此高版本Http使用Cache-Control替代Cache-Control:取值如下no-cache:不使用缓存,每次都从服务器获取no-store:不进行缓存max-age=60,表示60秒之后缓存过期public:客户端和服务器、CDN等都可以缓存private:只能被客户端缓存
Last-Modified:服务端返回上一次修改时间,客户端将缓存标识和数据一起缓存If-Modified-Since:客户端将缓存的标识发给服务端,由服务端判断是否过期,返回304状态码,表示客户端可以使用缓存数据ETag:服务端返回资源在服务器的唯一标识,客户端缓存下来If-None-Match:客户端再次请求服务器时,通过此字段将ETag唯一标识发给服务端,服务端将该字段和请求的资源标识对比,不同则说明被修改过,返回200,相同则说明没被修改过,返回304,告知客户端可以使用缓存
ETag/If-None-Match优先级高于Last-Modified/If-Modified-Since304表示
Not Modified
OkHttp
OkHttp本质是对Http协议的封装和解析,将数据段和Java对象互相转换,便于Java代码访问和处理
例如Request、Response,HttpUrl、Header、RequestBody等
如果没有这些类,则需要开发者自行分割字符串,进行解析
Request
Request存储一次Http请求信息
public final class Request {
final HttpUrl url;
final String method; // 请求方式
final Headers headers; // 请求头
final @Nullable RequestBody body; // 请求体
final Object tag;
private volatile CacheControl cacheControl; // 缓存控制字段
...
public static class Builder {
...
//设置cacheControl时,会转为字符串存到Header
public Builder cacheControl(CacheControl cacheControl) {
String value = cacheControl.toString();
if (value.isEmpty()) return removeHeader("Cache-Control");
return header("Cache-Control", value);
}
}
}
CacheControl其实是Header中的字段,设置cacheControl最终会写到Header中,使用的时候也可以从Header中解析。
为什么独立出来一个CacheControl类?
对于简单的字段,Header直接key-value存储即可。对于复杂的字段,由开发者自己编辑value字符串,或者从字符串中解析较麻烦,而且也难以记忆,因此提供对象的方式访问。
Header
Header中存储Http请求头信息:本质是key-value
- 构造过程中使用列表添加,build之后会转为数组
- 使用数组而不是Map存储,偶数下标存储key,奇数下标存储value
public final class Headers {
private final String[] namesAndValues;
Headers(Builder builder) {
this.namesAndValues = builder.namesAndValues.toArray(new String[builder.namesAndValues.size()]);
}
//按行传入,根据冒号分割key-value
public Builder add(String line) {
int index = line.indexOf(":");
if (index == -1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unexpected header: " + line);
}
return add(line.substring(0, index).trim(), line.substring(index + 1));
}
public Builder add(String name, String value) {
//检查是否存在非法字符
checkNameAndValue(name, value);
return addLenient(name, value);
}
Builder addLenient(String name, String value) {
namesAndValues.add(name);
namesAndValues.add(value.trim());
return this;
}
public static final class Builder {
final List<String> namesAndValues = new ArrayList<>(20);
}
}
CacheControl
CacheControl描述Header中的Cache-Control字段信息
- 构造方法私有,只能使用
Builder创建 - 提供了两个预置的
CacheControl对象:FORCE_NETWORK:强制使用网络响应数据FORCE_CACHE:强制使用缓存数据,如果缓存不可用,则返回504状态码
public final class CacheControl {
//强制使用网络响应数据
public static final CacheControl FORCE_NETWORK = new Builder().noCache().build();
//强制使用缓存数据,即使缓存已经过期,如果缓存不可用,则返回504状态码
public static final CacheControl FORCE_CACHE = new Builder()
.onlyIfCached()
.maxStale(Integer.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
private final boolean noCache; // 不使用缓存,使用网络响应
private final boolean noStore; // 不存储缓存数据
private final int maxAgeSeconds; // 设置缓存最大存活时间,超过该时间会重新发起请求,缓存时间不能超过Int范围
private final int sMaxAgeSeconds;
private final boolean isPrivate; // 只允许客户端缓存
private final boolean isPublic; // 客户端和服务器都可以缓存
private final boolean mustRevalidate;
private final int maxStaleSeconds; // 可以接收的响应的最大过期时间,默认不接收过期响应
private final int minFreshSeconds; // 响应保持新鲜的最小时间,小于该时间时不会重新发起网络请求
private final boolean onlyIfCached; // 只接收缓存中的响应,如果没有缓存,会返回504状态码
private final boolean noTransform;
private final boolean immutable; // 数据不会被修改,缓存始终有效
private CacheControl(boolean noCache, boolean noStore, int maxAgeSeconds, int sMaxAgeSeconds,
boolean isPrivate, boolean isPublic, boolean mustRevalidate, int maxStaleSeconds,
int minFreshSeconds, boolean onlyIfCached, boolean noTransform, boolean immutable,
@Nullable String headerValue) {
...
}
CacheControl(Builder builder) {
...
}
}
Cache
- InternelCache:是一个接口,只能在OkHttp内部使用,没有具体实现,都是调用Cache类
- DiskLruCache:磁盘缓存类,封装了读写文件等操作
- Cache:缓存管理类,管理
InternalCache和DiskLruCache
// Cache类无法被继承
public final class Cache implements Closeable, Flushable {
private static final int VERSION = 201105;
private static final int ENTRY_METADATA = 0;
private static final int ENTRY_BODY = 1;
private static final int ENTRY_COUNT = 2;
final InternalCache internalCache = new InternalCache() {
@Override public Response get(Request request) throws IOException {
return Cache.this.get(request);
}
...
};
final DiskLruCache cache;
/* read and write statistics, all guarded by 'this' */
int writeSuccessCount;
int writeAbortCount;
private int networkCount;
private int hitCount;
private int requestCount;
// 指定缓存路径和数量
public Cache(File directory, long maxSize) {
this(directory, maxSize, FileSystem.SYSTEM);
}
Cache(File directory, long maxSize, FileSystem fileSystem) {
this.cache = DiskLruCache.create(fileSystem, directory, VERSION, ENTRY_COUNT, maxSize);
}
}
这里需要注意的是使用方式:OkHttpClient.Builder().cache(new Cache(File, maxSize))指定缓存路径
InternalCache为OkHttp内部使用的类,没有提供接口让外部设置InternalCache- 由于
Cache类被声明为final,因此只能使用OkHttp提供的Cache类,无法自定义实现
缓存策略
客户端验证缓存是否有效,决定是否发出网络请求。主要由两个变量控制
networkRequest:为null表示不需要发出请求,only-if-cachedcacheResponse:为null表示无缓存或者缓存失效
public final class CacheStrategy {
/** The request to send on the network, or null if this call doesn't use the network. */
public final @Nullable Request networkRequest;
/** The cached response to return or validate; or null if this call doesn't use a cache. */
public final @Nullable Response cacheResponse;
}
存在4种情况
| networkRequest | cacheResponse | 结果 |
|---|---|---|
| null | null | 不进行网络请求,且缓存无效,一定会返回504 |
| null | non-null | 不进行网络请求,且缓存有效,直接返回缓存 |
| non-null | null | 缓存无效,直接发出网络请求 |
| non-null | non-null | 需要协商缓存,发出网络请求,由服务器根据ETag、Last-Modified等标签验证缓存是否有效 |
缓存策略的选择:解析Header中的缓存字段(规则比较长,可以跳过)
public final class CacheStrategy {
public static class Factory {
public Factory(long nowMillis, Request request, Response cacheResponse) {
this.nowMillis = nowMillis;
this.request = request;
this.cacheResponse = cacheResponse;
if (cacheResponse != null) {
//从缓存的响应中解析出Header中的缓存设置,例如ETag、Date、Expires、Last-Modified等字段
}
}
// 创建对应的缓存策略
public CacheStrategy get() {
CacheStrategy candidate = getCandidate();
// 强制使用缓存,并且缓存无效,返回504
if (candidate.networkRequest != null && request.cacheControl().onlyIfCached()) {
return new CacheStrategy(null, null);
}
return candidate;
}
private CacheStrategy getCandidate() {
// 无缓存,直接使用网络请求
if (cacheResponse == null) {
return new CacheStrategy(request, null);
}
// Drop the cached response if it's missing a required handshake.
if (request.isHttps() && cacheResponse.handshake() == null) {
return new CacheStrategy(request, null);
}
// noStore不缓存数据情况下,使用网络请求
if (!isCacheable(cacheResponse, request)) {
return new CacheStrategy(request, null);
}
// noCache或者ETag、Last-Modified为空,使用网络请求
CacheControl requestCaching = request.cacheControl();
if (requestCaching.noCache() || hasConditions(request)) {
return new CacheStrategy(request, null);
}
CacheControl responseCaching = cacheResponse.cacheControl();
// 数据不会被修改,缓存始终有效
if (responseCaching.immutable()) {
return new CacheStrategy(null, cacheResponse);
}
long ageMillis = cacheResponseAge();
long freshMillis = computeFreshnessLifetime();
if (requestCaching.maxAgeSeconds() != -1) {
freshMillis = Math.min(freshMillis, SECONDS.toMillis(requestCaching.maxAgeSeconds()));
}
long minFreshMillis = 0;
if (requestCaching.minFreshSeconds() != -1) {
minFreshMillis = SECONDS.toMillis(requestCaching.minFreshSeconds());
}
long maxStaleMillis = 0;
if (!responseCaching.mustRevalidate() && requestCaching.maxStaleSeconds() != -1) {
maxStaleMillis = SECONDS.toMillis(requestCaching.maxStaleSeconds());
}
if (!responseCaching.noCache() && ageMillis + minFreshMillis < freshMillis + maxStaleMillis) {
Response.Builder builder = cacheResponse.newBuilder();
if (ageMillis + minFreshMillis >= freshMillis) {
builder.addHeader("Warning", "110 HttpURLConnection \"Response is stale\"");
}
long oneDayMillis = 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000L;
if (ageMillis > oneDayMillis && isFreshnessLifetimeHeuristic()) {
builder.addHeader("Warning", "113 HttpURLConnection \"Heuristic expiration\"");
}
//根据时间本地验证缓存是否失效
return new CacheStrategy(null, builder.build());
}
// Find a condition to add to the request. If the condition is satisfied, the response body
// will not be transmitted.
String conditionName;
String conditionValue;
if (etag != null) {
conditionName = "If-None-Match";
conditionValue = etag;
} else if (lastModified != null) {
conditionName = "If-Modified-Since";
conditionValue = lastModifiedString;
} else if (servedDate != null) {
conditionName = "If-Modified-Since";
conditionValue = servedDateString;
} else {
//没有可以用于协商的字段,使用网络请求
return new CacheStrategy(request, null); // No condition! Make a regular request.
}
Headers.Builder conditionalRequestHeaders = request.headers().newBuilder();
Internal.instance.addLenient(conditionalRequestHeaders, conditionName, conditionValue);
// 协商缓存请求
Request conditionalRequest = request.newBuilder().headers(conditionalRequestHeaders.build())
.build();
return new CacheStrategy(conditionalRequest, cacheResponse);
}
}
缓存流程
- 根据url从
DiskLruCache中读取缓存的响应 - 根据
Cache-Control缓存配置、缓存验证等来创建对应的缓存策略 - 强制缓存,但缓存无效,返回504响应
- 强制缓存,且缓存有效,返回缓存的响应
- 协商缓存或者缓存无效情况下,进行网络请求,交给下一个责任链
- 协商缓存验证缓存有效,返回缓存的响应,并更新缓存
- 协商缓存验证无效,使用新的网络响应,并缓存该响应
上面提到的缓存无效包括过期、被修改或者无缓存等情况
public final class CacheInterceptor implements Interceptor {
final InternalCache cache;
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
// 根据url从DiskLruCache中读取缓存的响应
Response cacheCandidate = cache != null ? cache.get(chain.request()) : null;
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 使用Factory创建缓存策略,根据Cache-Control缓存配置等因素决定
CacheStrategy strategy = new CacheStrategy.Factory(now, chain.request(), cacheCandidate).get();
Request networkRequest = strategy.networkRequest;
Response cacheResponse = strategy.cacheResponse;
if (cache != null) {
cache.trackResponse(strategy);
}
// 缓存策略判断取出的缓存不可用,则关闭该流
if (cacheCandidate != null && cacheResponse == null) {
closeQuietly(cacheCandidate.body()); // The cache candidate wasn't applicable. Close it.
}
// 如果不允许使用网络请求,并且缓存无效,则返回504
if (networkRequest == null && cacheResponse == null) {
return new Response.Builder().request(chain.request()).protocol(Protocol.HTTP_1_1)
.code(504)
.message("Unsatisfiable Request (only-if-cached)")
.body(Util.EMPTY_RESPONSE)
.sentRequestAtMillis(-1L)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build();
}
// 强制缓存,不需要经过网络,且缓存有效,直接返回本地缓存的响应
if (networkRequest == null) {
return cacheResponse.newBuilder().cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse)).build();
}
Response networkResponse = null;
try {
// 协商缓存或者无本地缓存情况下,需要请求网络
networkResponse = chain.proceed(networkRequest);
} finally {
// If we're crashing on I/O or otherwise, don't leak the cache body.
if (networkResponse == null && cacheCandidate != null) {
closeQuietly(cacheCandidate.body());
}
}
if (cacheResponse != null) {
// 协商缓存服务器验证有效,则使用缓存的响应,并更新响应头和数据
if (networkResponse.code() == HTTP_NOT_MODIFIED) {
Response response = cacheResponse.newBuilder()
.headers(combine(cacheResponse.headers(), networkResponse.headers()))
.sentRequestAtMillis(networkResponse.sentRequestAtMillis())
.receivedResponseAtMillis(networkResponse.receivedResponseAtMillis())
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.networkResponse(stripBody(networkResponse))
.build();
networkResponse.body().close();
// 更新缓存
cache.trackConditionalCacheHit();
cache.update(cacheResponse, response);
return response;
} else {
closeQuietly(cacheResponse.body());
}
}
// 协商缓存无效,或者无缓存情况下,使用新的网络响应
Response response = networkResponse.newBuilder()
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.networkResponse(stripBody(networkResponse))
.build();
if (cache != null) {
if (HttpHeaders.hasBody(response) && CacheStrategy.isCacheable(response, networkRequest)) {
// 加入缓存
CacheRequest cacheRequest = cache.put(response);
return cacheWritingResponse(cacheRequest, response);
}
if (HttpMethod.invalidatesCache(networkRequest.method())) {
try {
cache.remove(networkRequest);
} catch (IOException ignored) {
// The cache cannot be written.
}
}
}
return response;
}
}
结语
https://www.jianshu.com/p/eca3d9371248
https://www.cnblogs.com/ganchuanpu/archive/2018/02/01/8399681.html