进程间通信又细分为不同场景
- 远程方法调用RPC:AIDL
- 跨进程消息通信:强调发送和接收消息,可以自定义消息结构,根据消息执行不同逻辑。Messenger
- 跨进程数据共享:ContentProvider
Binder、Socket、管道、信号量等
由于Binder驱动的限制,传输数据不能超过1M-8K,否则会抛出TransactionTooLargeException异常。
-8K是为了添加一个内存保护页
对于大数据传输,可以使用共享内存,没有大小限制。
跨进程传输Bitmap:https://blog.csdn.net/ylyg050518/article/details/97671874
- 使用共享内存
- 使用
Intnent.putBinder方法,内部也是开辟了共享内存,调用writeBlob
匿名共享内存
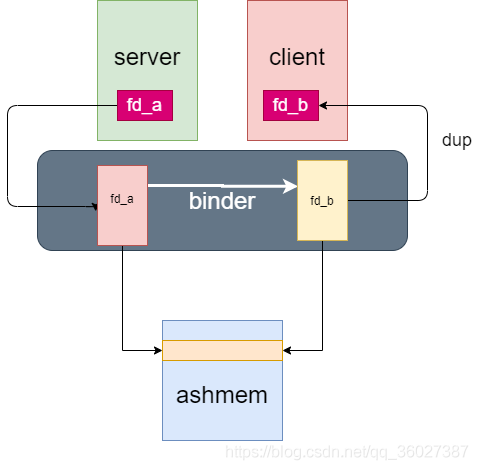
Android提供了共享内存机制——Ashmem(Anonymous Shared Memory,匿名共享内存),基于Linux的mmap系统调用,可以将同一段物理内存映射到不同进程各自的虚拟地址空间,实现高效的进程间共享。
原理:
- A进程创建共享内存,写入数据
- 通过Binder跨进程传递共享内存的文件描述符FD(句柄)
- B进程通过句柄读取共享内存数据。
使用方式
C++
使用IAllocator、IMemory、hidl_memory、hidl_handle等接口实现共享内存。Java层也封装了对应的接口
Java
封装了MemoryFile或SharedMemory类,本质也是调用native方法
首先写一个服务端,这个服务端中在远程调用的的时候,要做以下事情:
- 创建一个匿名共享内存
- 往这个共享内存中写一个字符数据
- 将这个匿名共享内存的文件句柄通过binder机制传递给客户端
package com.kobe.ashmen;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.MemoryFile;
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.ParcelFileDescriptor;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import java.io.FileDescriptor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class RemoteService extends Service {
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return new MyBinder();
}
public class MyBinder extends Binder {
@Override
protected boolean onTransact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags) throws RemoteException {
if (code == 1) {
try {
String str = "kobewang";
byte[] contentBytes = str.getBytes();
//创建匿名共享内存
MemoryFile mf = new MemoryFile("memfile", contentBytes.length);
//写入字符数据
mf.writeBytes(contentBytes, 0, 0, contentBytes.length);
Method method = MemoryFile.class.getDeclaredMethod("getFileDescriptor");
//通过反射获得文件句柄
FileDescriptor fd = (FileDescriptor) method.invoke(mf);
ParcelFileDescriptor pfd = ParcelFileDescriptor.dup(fd);
//将文件句柄写到binder调用的返回值中。
reply.writeFileDescriptor(fd);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}
}
}
再写一个客户端,主要做以下事情:
- bindservice获得服务端的binder对象
- 调用binder的接口获得服务端匿名共享内存的文件句柄
- 通过文件句柄,直接访问匿名共享内存中的数据,并打印出log。
package com.kobe.ashmen;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileDescriptor;
import java.io.FileReader;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//绑定服务
Intent intent = new Intent(this, RemoteService.class);
bindService(intent, new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
try {
//通过binder机制跨进程调用服务端的接口
service.transact(1, data, reply, 0);
//获得RemoteService创建的匿名共享内存的fd
FileDescriptor fd = reply.readFileDescriptor().getFileDescriptor();
//读取匿名共享内存中的数据,并打印log
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fd));
Log.v("kobe-result", br.readLine());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
}
}, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
}
注册服务端,指定新进程
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.kobe.ashmen">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service
android:name=".RemoteService"
android:process=":RemoteService" />
</application>
</manifest>
案例
- Android的
SurfaceFlinger服务:APP进行渲染,将绘制信息保存到应用进程的共享内存映射中,SurfaceFlinger进程收集各个窗口视图,合成最终的画面。
FileProvider
FileProvider也是通过跨进程传递文件FD,从而读取文件流。
早期的安卓系统通过file://类型的Uri来访问其他应用的文件,应用需要修改文件的系统访问权限,这样会导致其他应用也能访问该文件。
Android 7.0 引入FileProvider,可以授予其他应用访问内部文件的临时权限,并且可随时撤销。
也可以授予永久权限:原理是写入
urigrants.xml文件,开机系统会读取该文件,进行授权。
用途:通过PackageInstaller程序安装应用内的APK、使用浏览器打开应用内的HTML文件、拍照预览、共享等
结语
参考资料: